ضماد الجرح الحروق
تُعد إصابات الحروق من أشد الإصابات الجسدية وأكثرها ضعفًا وتؤثر على كل جهاز عضو تقريبًا وتؤدي إلى ارتفاع معدل الوفيات والمراضة. يعتبر الاستئصال المبكر للحروق وتطعيم الجلد من العلاجات السريرية القياسية التي أدت إلى تحسين النتائج بشكل كبير للمرضى الذين يعانون من إصابات الحروق الشديدة من خلال تقليل الوفيات وأيام المستشفى. ومع ذلك ، في إدارة وبحوث الحروق ، يظل تلف الجلد ، والألم ، والعدوى ، وبطء التئام الجروح ، وفقدان السوائل ، والعدوى البكتيرية ، واختيار المواد المناسبة لضمادات جروح الحروق تحديًا كبيرًا.
الخصائص المثالية لتضميد جرح الحروق
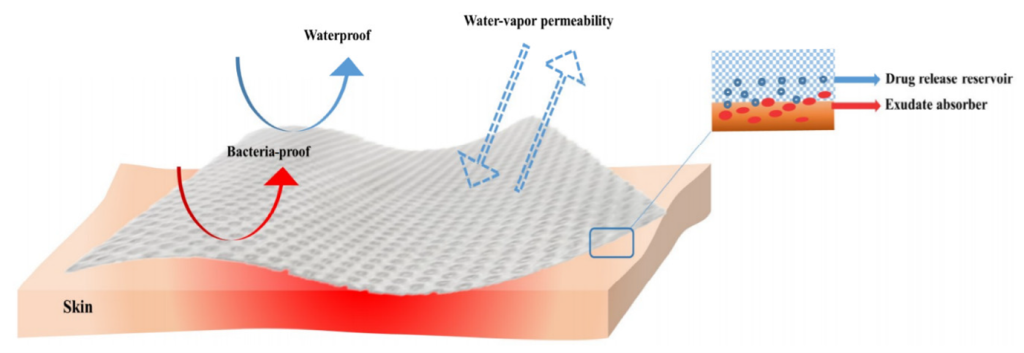
يجب تصميم ضمادات الحروق لخلق بيئة يمكن أن يحدث فيها التئام الجروح ، وهذه الخاصية معروفة جيدًا لضمادات الحروق. ولعل أهم ما يميز الضمادة هي قدرتها على تنظيم توازن السوائل. أثناء جرح الحرق ، يُفقد الكثير من السوائل من خلال التبخر ومن خلال النضح ، لذا فإن إدارة السوائل مهمة جدًا في إصابات الحروق. يزيد من التمثيل الغذائي ويخفض درجة حرارة الجسم. يجب أن تكون وظيفة الضمادة هي امتصاص السوائل والتحكم في نقلها للحفاظ على رطوبة الجرح لأن الرطوبة العالية تسبب التحبيب وتساعد على التكون الظهاري. يجب أن تكون الخاصية اللاصقة لضمادة الجرح جيدة أيضًا لتجنب مشاكل الانزلاق من موقع الحرق. مطلوب التصاق موحد لمنع تسرب السوائل وانتشارها بسبب نمو البكتيريا. التصاق ضمادة الجرح مع الإفرازات الجافة (dry exudate)أمر غير مرغوب فيه ، سيكون مؤلمًا وقد يؤدي إلى تلف الأنسجة. علاوة على ذلك ، لن يكون من السهل إزالته. لذلك ، من أجل مراعاة راحة المريض ، يجب أن تكون إزالة الضمادة سهلة وغير مؤلمة.
| Ideal properties of burn wound dressings الخصائص المثالية لتضميد جرح الحروق | |
| Absorbency | Gaseous exchange |
| Adherence | Hemostatic |
| Barrier against bacteria | Non-allergic |
| Comfortability | Non-carcinogenic |
| Drug delivery | Non-toxic |
| Durability | Non-antigenic |
| Easy to remove and applied | Sterilization ability |
| Elasticity | Water vapor transmissibility |
Classification of burn wound dressings
تصنيف ضمادات الحروق
يمكن تصنيف ضمادات جروح الحروق حسب استخدامها إلى ثلاث فئات رئيسية:
- Conventional dressings
- الضمادات التقلیدیة
الضمادات التقليدية أو Conventional dressings في بعض الأحيان هي الضمادات الشائعة الاستخدام لجميع أنواع الجروح. تتميز الضمادات التقليدية بقدرة عالية على الامتصاص وهيكل جيد يمنع التجمع ويمنعه. لذلك ، يتوزع السائل الممتص بانتظام في جميع أنحاء مادته..
الشاش هو المادة التي تلبي هذه المتطلبات ويتم ملاحظتها بشكل متكرر على أنها أكثر الضمادات الماصة المقبولة والمتوفرة حاليًا. نظرًا لأن سعر الشاش منخفض جدًا ، فهو الضمادة الماصة الأكثر شيوعًا والأكثر استخدامًا كمركب من صوف الشاش القطني.

مثال نموذجي على هذا الضماد هو وسادة الأنسجة

في هذا الضماد ، يتم وضع طبقة (مركبة) من القطن والصوف بين ملاءات الشاش. يتم قياس قدرة امتصاص هذه الضمادة بسماكة وحجم طبقة الصوف القطني. لمنع الصدمات والألم ، يجب إزالة الطبقة الداخلية من هذه الضمادة بسهولة ويجب أن تكون غير ملتصقة.
يمكن أن تكون العدوى الناتجة عن تلوث الإفرازات من خلال شبكة الشاش المفتوحة مشكلة في هذه الضمادات.
- Biological dressings
الضمادات البيولوجية
تُشتق الضمادات البيولوجية من الأنسجة الطبيعية ، عادةً الجلد ، وتتألف من تركيبات مختلفة من الإيلاستين والدهون والكولاجين. تُعزى الضمادات البيولوجية إلى العديد من التأثيرات المفيدة على الضمادات الاصطناعية التي تقلل من تعداد البكتيريا على سطح الجرح ، وتقلل من الجفاف ، وتقلل من فقد الماء وفقدان حرارة التبخر ، وتمنع الجرح من المزيد من التلوث ، وتخلق طبقة حبيبية جيدة من الأنسجة للجروح العميقة وتحسينها.
- Allografts
• الطعم الذاتي هو أكثر طرق الكسب غير المشروع شيوعًا التي تستخدم في ضمادات جروح الحروق
• في حالة الحروق الشديدة ، يمكن أن يكون مصدر ترقيع الجلد غير كامل ويتم البحث عن أنسجة من مصدر آخر
• الجلد المستخدم كطعم خيفي يتم اكتسابه من فرد من العائلة أو من شخص آخر خارج العائلة
- Xenografts
• الطعوم من الحيوانات
• يستخدم جلد الخنزير كطعم أجنبي شائع (طعم أجنبي للخنازير)
• يوفر جلد الخنزير ضمادة معقمة وسهلة التخزين ومتاحة بسهولة ، على عكس جلد الخيفي.
• جلد الخنزير يختلف عن جلد الإنسان تحت المستوى المجهري. ومع ذلك ، فهو متشابه جدًا من حيث الالتصاق والملمس ومواد الكولاجين.
• أحد الجوانب السلبية الكبيرة لطعم أجنبي الخنازير المجفف بالتجميد هو أن هناك حاجة لإعادة بنائه عن طريق النقع في محلول ملحي أو محلول ملحي معقم قبل الاستخدام. تستغرق هذه العملية حوالي 30 دقيقة عند 30 درجة مئوية مما يؤدي إلى تأخير كبير في علاج جروح الحروق.
• طعوم xenografts من الخنازير ليس لها خصائص ميكانيكية جيدة وتتكسر بشكل عام إلى طبقات مختلفة ، مما يمنع أخذ الجلد الذاتي.
Tissue derivatives
مشتقات الأنسجة
كضمادة بيولوجية ، للكولاجين العديد من المزايا. نظرًا لأنه يمكن تنقيته وعزله بسرعة بكميات كبيرة ، يمكن تعديل نفاذية بخار الماء واستضداده.
تثير هذه الضمادات السرير الوعائي المحبب استعدادًا للطعم الذاتي المحتمل. يتمثل الجانب السلبي الأساسي للتطبيق طويل الأمد لضمادات الكولاجين في مكافحة العدوى.
- synthetic dressings
الضمادات الاصطناعية
تم تطوير مواد تركيبية مختلفة لتضميد الجروح لجعلها منخفضة التكلفة وفعالة للغاية وتخزينها بسهولة لفترة طويلة.
تنقسم الضمادات الاصطناعية أيضًا إلى الفئات التالية: الرغاوي والبخاخات والأفلام والمركبات والمواد الهلامية.
Foams and sprays
الرغاوي والبخاخات
• في الوقت الحالي ، يشيع استخدام رغاوي البولي يوريثين وكحول البولي فينيل.
• ضمادة الجرح بالرش لها ميزتان رئيسيتان ، فهي جاهزة للاستخدام تحت أي ظرف من الظروف ، والميزة الأخرى لهذا الضمادة مريحة.
• عيوب الضمادة القائمة على الرش هي السمية عند ملامستها للأوعية الدموية

- Films
أفلام
• تمت دراسة مواد مختلفة لتضميد جرح الحروق. بعضها عبارة عن أغشية تستخدم في تغليف المواد الغذائية (على سبيل المثال ، رقائق التغليف).
• يشيع استخدام الأغشية المرنة المصنوعة من السيليكون ، وكانت النتائج التي تم الحصول عليها مواتية وجيدة.
• الأغشية البوليمرية الأخرى التي يمكن استخدامها كضماد للجرح هي البولي إيثيلين ، وحمض البولي لاكتيك ، والبولي يوريثين ، وبولي تترافلورو إيثيلين ، وأكريلونيتريل كوبوليمر ، وبولي أمينو أسيد ، وثنائي ميثيل أمينو إيثيل ميثاكريلات.
• المشكلة في بعض ضمادات الجروح هي عدم القدرة على الاحتفاظ بالإفرازات
• على سبيل المثال ، ضمادة الجرح tegaderm لها كيس لامتصاص الإفرازات الزائدة

Composites
المركبات
• المركب عبارة عن هيكل مصفح يتكون من مادتين أو أكثر.
• في هذه الضمادة ، يكون الهيكل الخارجي مسؤولاً عن المرونة والمتانة. وتتمثل وظيفتها في التحكم في تدفق بخار الماء ، بينما الغرض من الطبقة الداخلية هو تحسين الالتصاق.
أبرز الأمثلة هي:
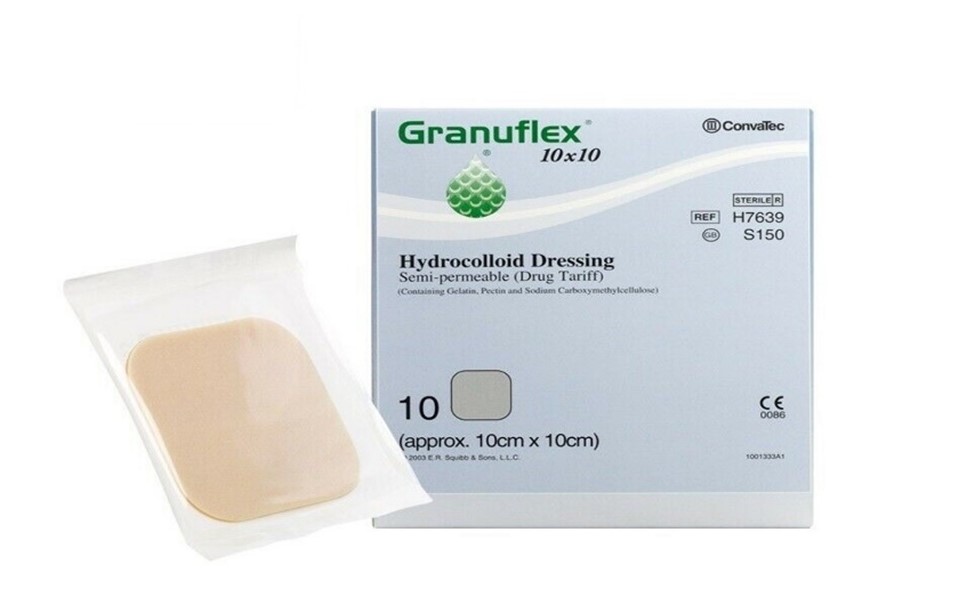
- جرانوفليكس(Granuflex)
تتكون هذه المادة من طبقة واقية خارجية رقيقة من رغوة البولي يوريثان وطبقة داخلية من غرواني مائي ، وهو مركب بوليمر
- Epigard
Epigard هو مركب يحتوي على مادة البولي يوريثين الشبكية كطبقة داخلية تم تصفيحها إلى صفيحة خارجية صغيرة يسهل اختراقها من البولي تترافلوروإيثيلين (PTFE). التكلفة المنخفضة ، العمر الافتراضي الطويل ، العقم ، التوافر ، والالتزام هي مزاياها.

• Biobrane
مركب به غشاء بولي ثنائي ميثيل سيلوكسان مسامي ورفيع للغاية مرتبط بشبكة داخلية من النايلون. من الدراسات المبكرة ، تم الكشف عن أن العدوى من البكتيريا كانت القضية الرئيسية في الاستخدام السريري لـ Biobrane

Gels
الهلام
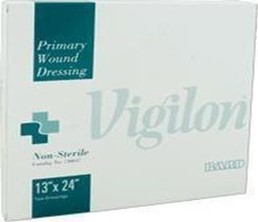
يتكون Vigilon ، وهو أحد المواد المتاحة تجاريًا للهيدروجيل ، من أكسيد البولي إيثيلين المدعوم بشبكة البولي إيثيلين ، والذي تم استخدامه مؤخرًا كضماد لجروح الحروق.
Omniderm هو أحد أكثر أنواع الجل الرقيق شفافًا والذي تم استخدامه كضمادة ، وقد توصل المصنعون إلى أنه يتم تثبيته في مكانه ويُسمح له بالبقاء في المكان المصاب حتى يتلاشى مع تقدم الشفاء.

Materials used in burn wound dressings
المواد المستخدمة في ضمادات جروح الحروق
تم استخدام بوليمرات طبيعية وصناعية مختلفة في ضمادات جروح الحروق.
• البوليمرات الطبيعية
- Natural polymers
تُستخدم البوليمرات الطبيعية على نطاق واسع في الطب التجديدي نظرًا لقدرتها على التحلل البيولوجي والتوافق الحيوي والتشابه مع المصفوفة خارج الخلية لضمادات الحروق. تشارك هذه البوليمرات في تجديد الجلد وإصلاح الأنسجة التالفة وتحفيز وإطلاق عملية التئام الجروح.
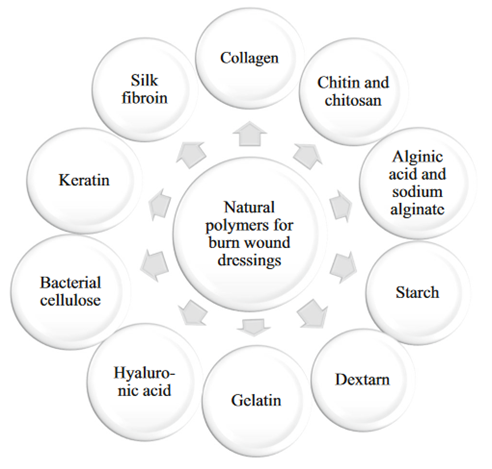
البوليمرات الطبيعية التي تستخدم في الغالب في تطوير ضمادات جروح الحروق
Synthetic polymers
البوليمرات الاصطناعية
تُستخدم بعض البوليمرات الاصطناعية على نطاق واسع في تطبيقات ضمادات الحروق ، نظرًا لخصائصها الفيزيائية والكيميائية والتوافق الحيوي.
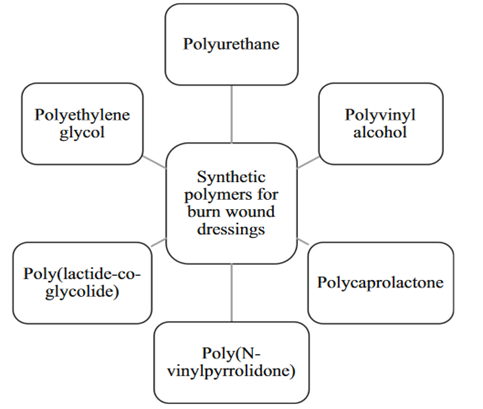
البوليمرات الاصطناعية الأكثر استخدامًا في تطوير ضمادات جروح الحروق
Burn wound dressing
Burn injuries are the most severe and physically debilitating injuries affecting almost every organ system resulting in high mortality and morbidity. Excision of early burn wounds and skin grafting are standard clinical treatments that have greatly improved the results for patients with serious burn injuries by reducing the mortality rate and hospital stay days. However, in burn management and research, skin damaging, pain, infection, slow wound healing, fluid loss, bacterial infection and selection of appropriate materials for burn wound dressings continue to remain a major challenge.
Ideal properties of burn wound dressings
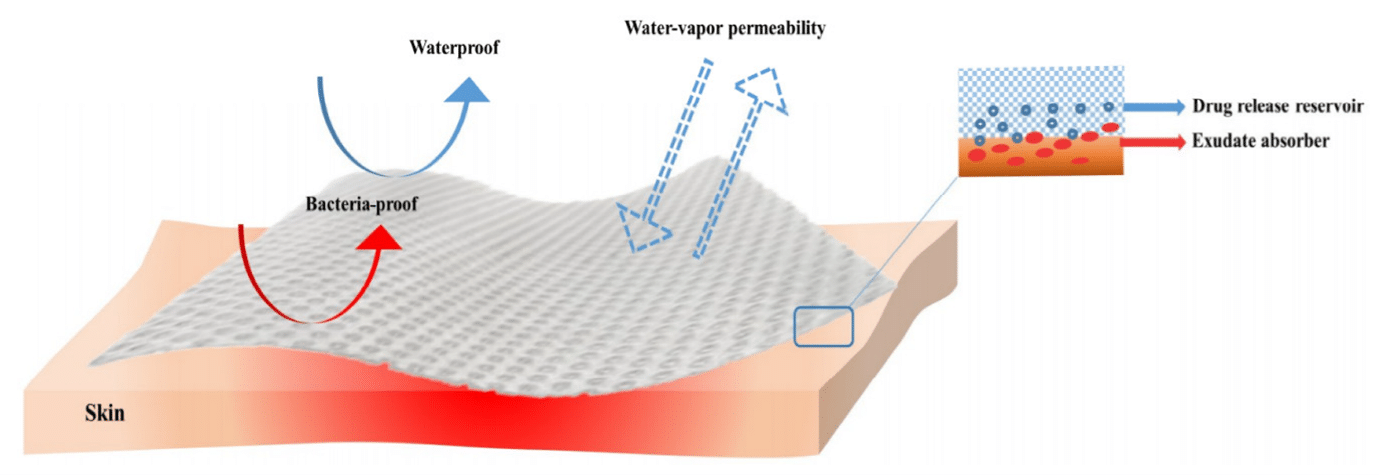
Burn dressings have to be designed to create an environment that enables healing process of wounds to occur, and these burn dressing specifications are well-known. A dressing probably has the most significant property of its ability to regulate fluid balance. During burn wound, through evaporation and through exudation, lots of fluid is waste so, manage fluid in burn injuries is very important. It leads to increase metabolic rate and reduce the body temperature. The functions of dressing must be to absorb the fluids and control its transmission to keep the wound humid because high humidity encourages granulation and assists epithelialization. Adhesion property of wound dressing must also be good to avoid the slipping and sliding problems from the burn site. Uniform adherence is required to avoid the fluid leakage and spreading due to proliferation of bacteria. Wound dressing adherence to dry exudate is undesirable, it will be painful, and it may damages tissues. Furthermore, its removal will not be so easy; therefore, for considering the comfort of patient dressing removal must be easy and free of pain.
| Ideal properties of burn wound dressings | |
| Absorbency | Gaseous exchange |
| Adherence | Hemostatic |
| Barrier against bacteria | Non-allergic |
| Comfortability | Non-carcinogenic |
| Drug delivery | Non-toxic |
| Durability | Non-antigenic |
| Easy to remove and applied | Sterilization ability |
| Elasticity | Water vapor transmissibility |
Classification of burn wound dressings
According to their usage, dressings for burn wounds can be classified into three main categories:
- Conventional dressings
Conventional dressings or sometimes traditional dressings are the commonly used dressings for all kinds of wounds. Conventional dressings have high capacity of absorbance and a good structure that avoids and prevents pooling. Therefore, absorbed fluid distributes regularly throughout its material.
Gauze is the material which meets these requirements and frequently observed as most acceptable absorbent dressing which is presently available. As price of gauze is very low, so, it is the most widely and commonly used absorptive dressing as a composite of gauze-cotton wool.
Typical example of this dressing is Gamgee tissue pad.


In this dressing, a layer (composite) of cotton and wool is placed between gauze’s sheets. Capacity of absorbance of this dressing is measured by thickness and volume of cotton wool layer. To prevent trauma and pain, the inner layer of this dressing should be easily removeable and must be non-adherent.
Infections due to exudate contamination through the open gauze network can be an issue with these dressings.
- Biological dressings
Biological dressings are derived from natural tissues, usually skin, consisting of different combinations and formulations of elastin, lipid and collagen. Biological dressings have been attributed to many beneficial effects over synthetic dressings that they reduce the population of bacteria on the surface of wound, reduce the desiccation, decrease water loss and evaporation heat loss, prevention wound from further contamination, create good tissue bed of granulation for deep wounds and improve healing.
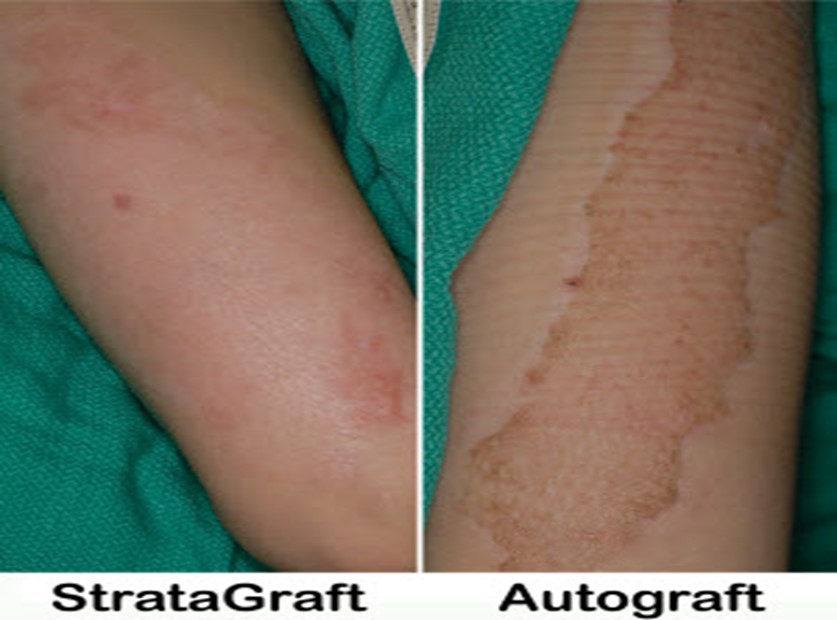
Allografts
- Autograft is the most common graft method that are used in burn wound dressings
- In case of severe burns, the source of split skin graft can be imperfect and tissue from another source has been sought
- Skin that used as an allograft skin is acquired from a person of a family or from another person outside the family
Xenografts
- Grafts from animals
- Pig skin is used as a common xenograft (porcine xenograft)
- Pig skin provides a sterilized, easily stored and readily available dressing, in contrast to allografts skin.
- Porcine skin is unlike the skin of human skin under microscopic level. It is however very similar in terms of adherence, texture and collagen material.
- One big downside with lyophilized porcine xenograft is that there is a need to reconstruct it by soaking in ringer or sterilized saline’s solution before use. This process takes about 30 min at 30 °C which results in a significant delay in burn wounds treatment.
- xenografts of porcine have no good mechanical properties and generally break into different layers, preventing autograft skin from being taken.

Tissue derivatives
As a biological dressing, collagen have many advantages. As it can be purified and isolated quickly in large quantity, its water vapor permeability and antigenicity can be modified.
These dressings arouse the granulated vascular bed in preparation for potential autograph grafting. The primary downside to long-term application of collagen dressings is infection control.

- synthetic dressings
Different synthetic materials have been developed for wound dressing to make it low cost, highly effective and stored easily for long time.
Synthetic dressings are further divided into following classes: foams and sprays, films, composites and gels.
Foams and sprays
- Currently, polyurethane and polyvinyl alcohol foams are commonly used.
- Spray-based wound dressing has two main advantages, it is ready to use under any circumstances, and the other advantage of this dressing is comfortable.
- The drawbacks of spray-based dressing are toxicity when in contact with blood vessels

Films
- Different materials have been studied for burn wound dressing. Some of them are films, used in food packing PVC (e.g., cling film).
- Elastomeric films made from silicone have been commonly used, and the obtained results were favorable and good.
- The other polymeric films which can be used as wound dressing are polyethylene, poly lactic acid, polyurethane, polytetrafluoroethylene, acrylonitrile copolymer, polyaminoacid, and dimethyl-amino-ethyl-methacrylate.
- The problem in some wound dressing are to fail in retention of exudate
- For example, tegaderm wound dressing has pouch to absorb the excessive exudate.

Composites
- Composite is the laminate structure of two or more materials.
- In this dressing, the outer structure is responsible for elasticity and durability ; its function is to control the flow of water vapor, while the purpose of inner layer is to improve the adherence.
The most notable examples are:
- Granuflex
This material is composed of a thin polyurethane foam’s outer protective layer and an inner layer of hydrocolloid, which is a polymer complex.

- Epigard
Epigard is a composite which have reticulated polyurethane as an inner layer that has been laminated to a microporous polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) outer sheet. Low cost, long shelf life, sterility, availability, and adherence are its advantages.

- Biobrane
A composite having porous and ultra-thin poly-dimethylsiloxane membrane bonded with an inner mesh of nylon. From the early studies, it is revealed that infection from bacteria was the main issue in Biobrane’s clinical use.

Gels
Vigilon, one of the commercially available material for hydrogel, consists of polyethylene oxide supported by polyethylene web, recently used as burn wound dressing.

Omniderm is one of most transparent thin gel that has been used as a dressing, and the manufacturers resulted that it is held in place and permissible to stay on the injured place until sloughed off by the healing progression.

Materials used in burn wound dressings
Different natural and synthetic polymers have been used in burn wound dressings.
- Natural polymers
Natural polymers are extensively used in regenerative medicine due to their biodegradability, biocompatibility and similarity with extracellular matrix for burn dressings. These polymers are implicated in skin regeneration, repairing damaged tissues, stimulating and triggering the process of wound healing.
Natural polymers that are used mostly in the development of burn wound dressings

Synthetic polymers
Some synthetic polymers are extensively used in burn dressing applications, due to their physicochemical and biocompatible properties.
Most commonly used synthetic polymers in the development of burn wound dressings


