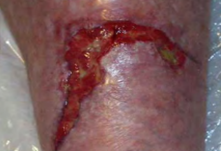
Chronic wounds represent a major public health issue, with an extremely high cost worldwide. In the USA, chronic wounds affect 1% of the total population, in Europe the incidence is 4 million cases per year which implies a rate of about 0.8%, in Australia 0.86%, in China 0.8–1%, and in India 0.6–1%. An ideal wound dressing should adhere to the wound surface and not to the wound bed, it should also be non-antigenic, biocompatible, semi-permeable, biodegradable, elastic but resistant, and cost-effective. The treatment of acute and chronic wounds is a pressing need and alginate-based wound dressings offer several advantages when compared to the traditional wound dressings.
Alginate is the most commonly biomaterial among other bioproducts with wound healing properties. Alginates are produced from the naturally occurring calcium and sodium salts of alginic acid found in a family of brown seaweed (Phaeophyceae). They generally fall into one of two kinds: those containing 100% calcium alginate or those that contain a combination of calcium with sodium alginate, usually in a ratio of 80:20. Alginates are rich in either mannuronic acid or guluronic acid, the relative amount of each influencing the amount of exudate absorbed and the shape the dressing will retain.
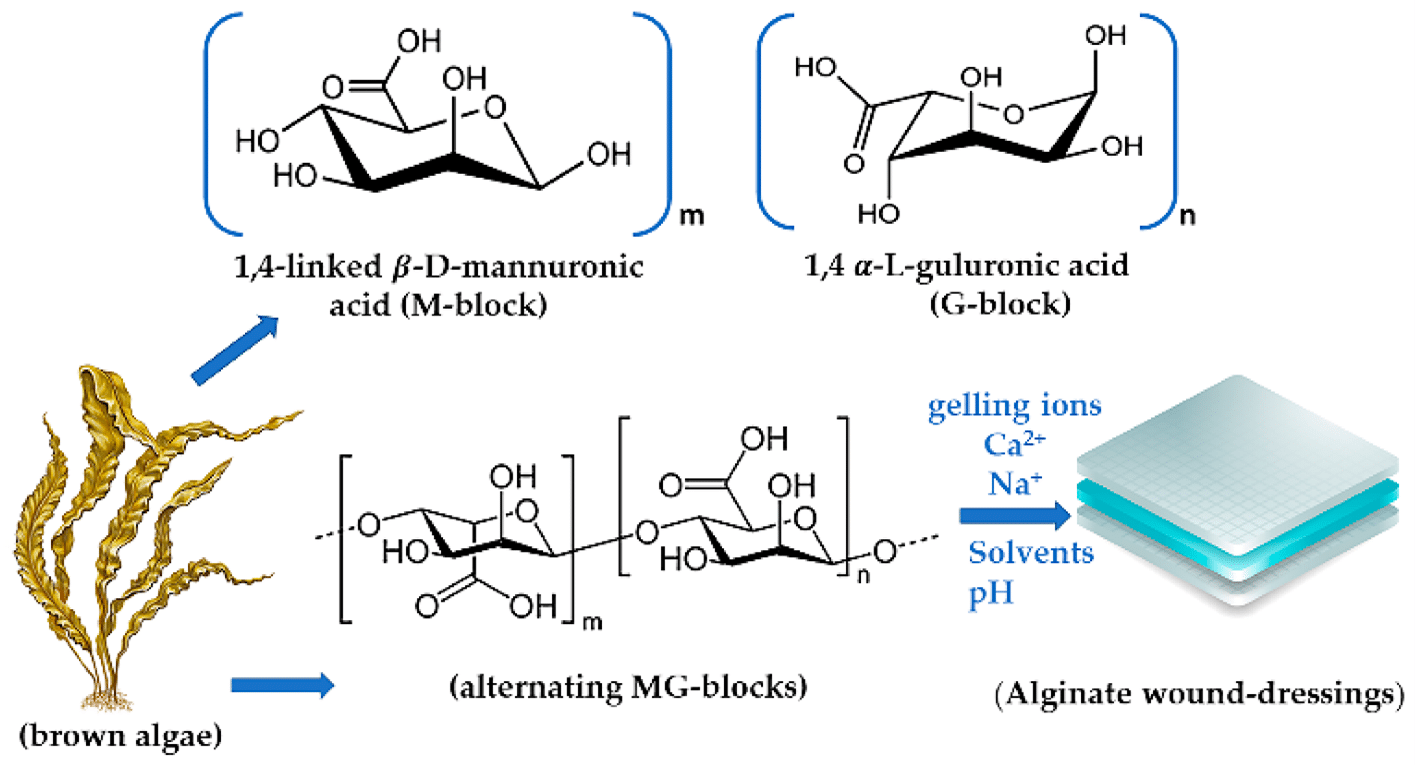
Alginates partly dissolve on contact with wound fluid to form a hydrophilic gel as a result of the exchange of sodium ions in wound fluid for calcium ions in the dressing. Those high in mannuronic acid (such as Kaltostat) can be washed off the wound easily with saline, but those high in guluronic acid (such as Sorbsan) tend to retain their basic structure and should be removed from the wound bed in one piece.
Alginate dressings exist in the form of hydrogels, films, foams, nanofibers, membrane, and sponges, etc. Alginate dressing is an absorbent dressing for moist wounds, composed of biodegradable, highly absorbent alginate fiber derived from seaweed, available in flat and rope patterns. In contact with exudate, these alginate dressings form a moist gel through ion exchange. The dressings are soft, conformable, and easy to apply in the cavity or irregular-shaped wounds. In addition, Alginate dressing enjoys excellent absorption and a good gel-forming effect. The alginate dressing consisting of calcium alginate provides superior absorption and is ideally designed for all moderate to heavily exuding both superficial and cavity wounds. The alginate dressing provides an ideal moist environment for healing, relieving wound pain.

What wounds do you use alginate on?
Yellow necrotic wound with high exudate
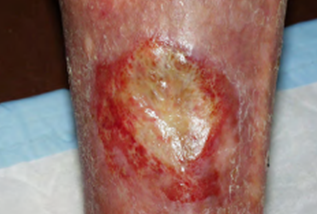
Cavity wound with high exudate
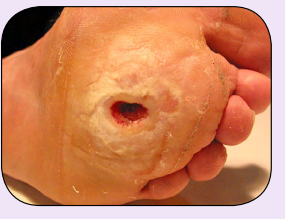
Exudating wound with slough and clinical signs of infection
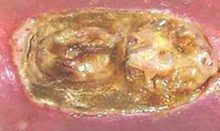
Cavity wound with low exudate
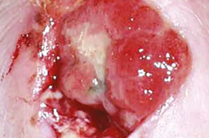
Superficial granulating wound with high exudate
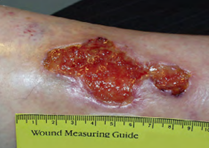
Malodorous wounds
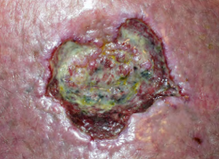
Superficial wound with clinical signs of infection
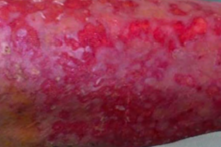
Skin tears